What Is The Current Carbon Dioxide Makeup Of The Atmosphere
CO2 Makes Up Just 0.04% of Earth'due south Atmosphere. Hither's Why Its Impact Is And then Massive
Reader question: I heard that carbon dioxide makes upwardly 0.04 percent of the world's atmosphere. Not 0.four percent or four percent, but 0.04 percentage! How can it be then important in global warming if it's such a small percentage?
I am often asked how carbon dioxide tin can have an important effect on global climate when its concentration is so modest – just 0.041 pct of World's atmosphere. And human activities are responsible for just 32 pct of that amount.
I study the importance of atmospheric gases for air pollution and climate change. The primal to carbon dioxide's stiff influence on climate is its ability to absorb heat emitted from our planet's surface, keeping it from escaping out to space.
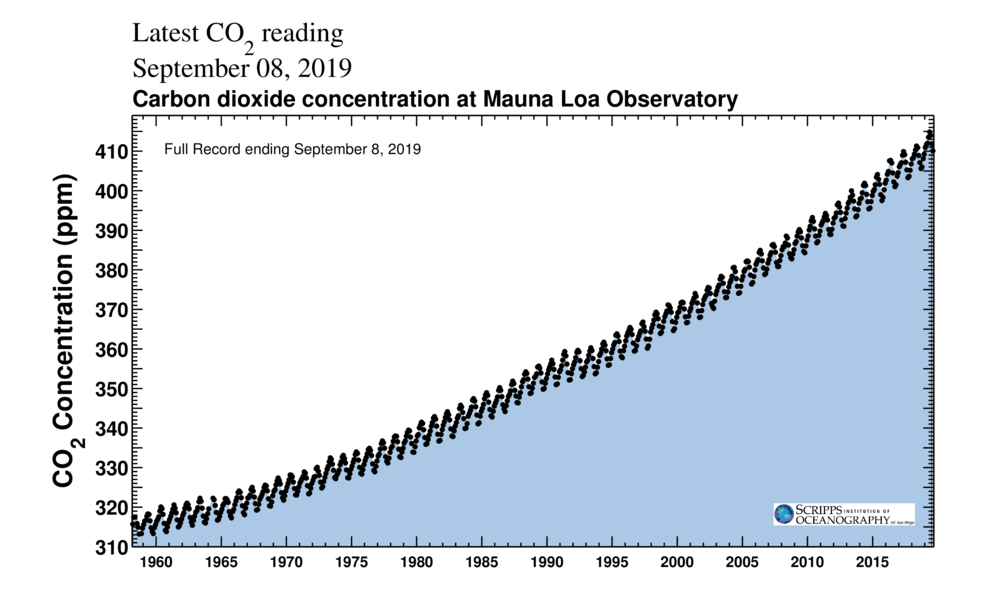 The 'Keeling Bend' tracks CO2 accumulation in Globe'southward temper. (Scripps Establishment of Oceanography/CC BY 4.0)
The 'Keeling Bend' tracks CO2 accumulation in Globe'southward temper. (Scripps Establishment of Oceanography/CC BY 4.0)
Early greenhouse science
The scientists who first identified carbon dioxide's importance for climate in the 1850s were likewise surprised by its influence. Working separately, John Tyndall in England and Eunice Foote in the U.s. plant that carbon dioxide, h2o vapor and marsh gas all absorbed estrus, while more abundant gases did not.
Scientists had already calculated that the Earth was virtually 59 degrees Fahrenheit (33 degrees Celsius) warmer than information technology should exist, given the corporeality of sunlight reaching its surface. The best caption for that discrepancy was that the atmosphere retained rut to warm the planet.
Tyndall and Foote showed that nitrogen and oxygen, which together business relationship for 99 percent of the temper, had essentially no influence on Earth'south temperature because they did not absorb rut.
Rather, they found that gases present in much smaller concentrations were entirely responsible for maintaining temperatures that made the Earth habitable, by trapping rut to create a natural greenhouse consequence.
A blanket in the temper
Earth constantly receives free energy from the Sun and radiates it back into infinite. For the planet'due south temperature to remain constant, the cyberspace heat information technology receives from the Sun must be balanced by approachable rut that it gives off.
Since the Dominicus is hot, it gives off energy in the course of shortwave radiation at mainly ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. Earth is much cooler, so it emits rut as infrared radiation, which has longer wavelengths.
Carbon dioxide and other heat-trapping gases have molecular structures that enable them to absorb infrared radiation. The bonds betwixt atoms in a molecule can vibrate in item ways, similar the pitch of a piano string. When the energy of a photon corresponds to the frequency of the molecule, it is captivated and its energy transfers to the molecule.
Carbon dioxide and other heat-trapping gases have 3 or more than atoms and frequencies that represent to infrared radiation emitted by Earth. Oxygen and nitrogen, with only ii atoms in their molecules, do not absorb infrared radiation.
Nearly incoming shortwave radiation from the Sun passes through the atmosphere without being absorbed.
Simply most outgoing infrared radiation is absorbed by estrus-trapping gases in the atmosphere. Then they tin release, or re-radiate, that heat. Some returns to Earth's surface, keeping information technology warmer than information technology would be otherwise.
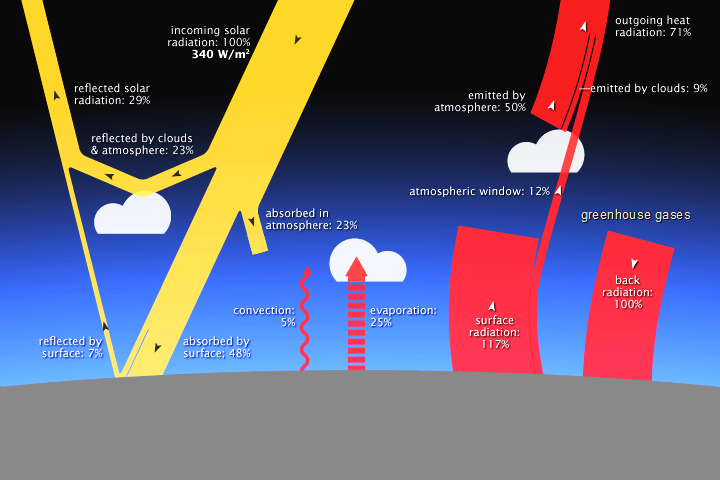 Solar radiation (xanthous) and radiating estrus (cherry-red) interacting with Earth. (NASA)
Solar radiation (xanthous) and radiating estrus (cherry-red) interacting with Earth. (NASA)
Enquiry on estrus transmission
During the Cold War, the absorption of infrared radiation by many unlike gases was studied extensively. The work was led by the U.s. Air Force, which was developing heat-seeking missiles and needed to empathise how to detect heat passing through air.
This inquiry enabled scientists to understand the climate and atmospheric composition of all planets in the Solar System past observing their infrared signatures. For example, Venus is about 870 F (470 C) because its thick temper is 96.5 percent carbon dioxide.
It also informed atmospheric condition forecast and climate models, allowing them to quantify how much infrared radiations is retained in the atmosphere and returned to Earth's surface.
People sometimes inquire me why carbon dioxide is important for climate, given that water vapor absorbs more infrared radiation and the two gases blot at several of the aforementioned wavelengths.
The reason is that Earth'southward upper atmosphere controls the radiation that escapes to infinite. The upper atmosphere is much less dense and contains much less water vapor than virtually the ground, which means that adding more carbon dioxide significantly influences how much infrared radiation escapes to infinite.
Observing the greenhouse upshot
Have you ever noticed that deserts are often colder at nighttime than forests, even if their boilerplate temperatures are the same? Without much water vapor in the atmosphere over deserts, the radiations they requite off escapes readily to infinite.
In more humid regions radiation from the surface is trapped by water vapor in the air. Similarly, cloudy nights tend to be warmer than articulate nights because more than water vapor is present.
The influence of carbon dioxide can exist seen in past changes in climate. Water ice cores from over the past million years have shown that carbon dioxide concentrations were loftier during warm periods – most 0.028 percent.
During ice ages, when Earth was roughly seven to 13 F (4-7 C) cooler than in the 20th century, carbon dioxide fabricated up only near 0.018 percent of the atmosphere.
Even though water vapor is more than important for the natural greenhouse effect, changes in carbon dioxide have driven past temperature changes. In contrast, h2o vapor levels in the atmosphere respond to temperature.
As Globe becomes warmer, its atmosphere can hold more water vapor, which amplifies the initial warming in a process chosen the "h2o vapor feedback." Variations in carbon dioxide have therefore been the decision-making influence on by climate changes.
Pocket-size change, big effects
It shouldn't be surprising that a small amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can accept a large effect. Nosotros take pills that are a tiny fraction of our body mass and expect them to affect us.
Today the level of carbon dioxide is higher than at any fourth dimension in human history. Scientists widely agree that Earth'southward average surface temperature has already increased by nearly 2 F (1 C) since the 1880s, and that man-caused increases in carbon dioxide and other heat-trapping gases are extremely likely to exist responsible.
Without action to control emissions, carbon dioxide might reach 0.1 per centum of the atmosphere by 2100, more than triple the level earlier the Industrial Revolution. This would exist a faster alter than transitions in Earth'southward past that had huge consequences.
Without action, this little sliver of the atmosphere will cause large problems.
Climate Explained is a collaboration betwixt The Conversation, Stuff and the New Zealand Scientific discipline Media Centre to answer your questions about climate change. ![]()
Jason West, Professor of Environmental Sciences and Technology, Academy of North Carolina at Chapel Colina.
This commodity is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source: https://www.sciencealert.com/co2-is-only-a-tiny-part-of-our-atmosphere-but-it-has-a-huge-influence-here-s-why
Posted by: bensonhaveracter.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Current Carbon Dioxide Makeup Of The Atmosphere"
Post a Comment